13 Agency and Employment
Learning Objectives
After reading this chapter, you should understand the following:
- Why agency is important, what an agent is, and the types of agents
- What an independent contractor is
- The duties owed by principals and agents
- The liability of principals and agents
- How common-law employment at will is modified by common-law doctrine, federal statutes, and state statutes
- Various kinds of prohibited discrimination under Title VII and examples of each kind
Introduction to Agency Law
Why Is Agency Law Important, and What Is an Agent?
An agent is a person who acts in the name of and on behalf of another, having been given and assumed some degree of authority to do so. Most organized human activity—and virtually all commercial activity—is carried on through agency. No corporation would be possible, even in theory, without such a concept. We might say “General Motors is building cars in China,” for example, but we can’t shake hands with General Motors. “The General,” as people say, exists and works through agents. Likewise, partnerships and other business organizations rely extensively on agents to conduct their business. Indeed, it is not an exaggeration to say that agency is the cornerstone of enterprise organization. In a partnership each partner is a general agent, while under corporation law the officers and all employees are agents of the corporation.
The existence of agents does not, however, require a whole new law of torts or contracts. A tort is no less harmful when committed by an agent; a contract is no less binding when negotiated by an agent. What does need to be taken into account, though, is the manner in which an agent acts on behalf of his principal and toward a third party.
Closely related to the idea, and its most common popular expression, is employment. Knowing the laws relating to the employment relationship are foundational to understanding the legal environment of business. These include the idea of employment at will and federal anti-discrimination law, which makes it unlawful to discriminate based on a number of protected attributes such as race and sex, which in 2020 was expanded by the Supreme Court to include sexual orientation.

Types of Agents
General Agent
The general agent possesses the authority to carry out a broad range of transactions in the name and on behalf of the principal. The general agent may be the manager of a business or may have a more limited but nevertheless ongoing role—for example, as a purchasing agent or as a life insurance agent authorized to sign up customers for the home office. In either case, the general agent has authority to alter the principal’s legal relationships with third parties. One who is designated a general agent has the authority to act in any way required by the principal’s business. To restrict the general agent’s authority, the principal must spell out the limitations explicitly, and even so the principal may be liable for any of the agent’s acts in excess of their authority.
Special Agent
The special agent is one who has authority to act only in a specifically designated instance or in a specifically designated set of transactions. For example, a real estate broker is usually a special agent hired to find a buyer for the principal’s land. Suppose Sam, the seller, appoints an agent Alberta to find a buyer for his property. Alberta’s commission depends on the selling price, which, Sam states in a letter to her, “in any event may be no less than $150,000.” If Alberta locates a buyer, Bob, who agrees to purchase the property for $160,000, her signature on the contract of sale will not bind Sam. As a special agent, Alberta had authority only to find a buyer; she had no authority to sign the contract.
Agency Coupled with an Interest
An agent whose reimbursement depends on their continuing to have the authority to act as an agent is said to have an agency coupled with an interest if he has a property interest in the business. A literary or author’s agent, for example, customarily agrees to sell a literary work to a publisher in return for a percentage of all monies the author earns from the sale of the work. The literary agent also acts as a collection agent to ensure that their commission will be paid. By agreeing with the principal that the agency is coupled with an interest, the agent can prevent their own rights in a particular literary work from being terminated to their detriment.
Employees
The final category of agent is an employee (please note, these can overlap, so that an employee could also be a general agent). An older term in the law is “servant”. Until the early nineteenth century, any employee whose work duties were subject to an employer’s control was called a servant; we would not use that term so broadly in modern English. The Restatement (Second) of Agency, Section 2, defines a servant as “an agent employed by a master [employer] to perform service in his affairs whose physical conduct in the performance of the service is controlled or is subject to the right to control by the master.”
Independent Contractor
Not every contract for services necessarily creates a master-servant or employment relationship. There is an important distinction made between the status of an employee and that of an independent contractor. According to the Restatement (Second) of Agency, Section 2, “an independent contractor is a person who contracts with another to do something for him but who is not controlled by the other nor subject to the other’s right to control with respect to his physical conduct in the performance of the undertaking.” As the name implies, the independent contractor is legally autonomous. A plumber salaried to a building contractor is an employee and agent of the contractor. But a plumber who hires himself out to repair pipes in people’s homes is an independent contractor. If you hire a lawyer to settle a dispute, that person is not your employee or your servant; she is an independent contractor. The terms “agent” and “independent contractor” are not necessarily mutually exclusive. In fact, by definition, “… an independent contractor is an agent in the broad sense of the term in undertaking, at the request of another, to do something for the other. As a general rule the line of demarcation between an independent contractor and a servant is not clearly drawn.”[1]

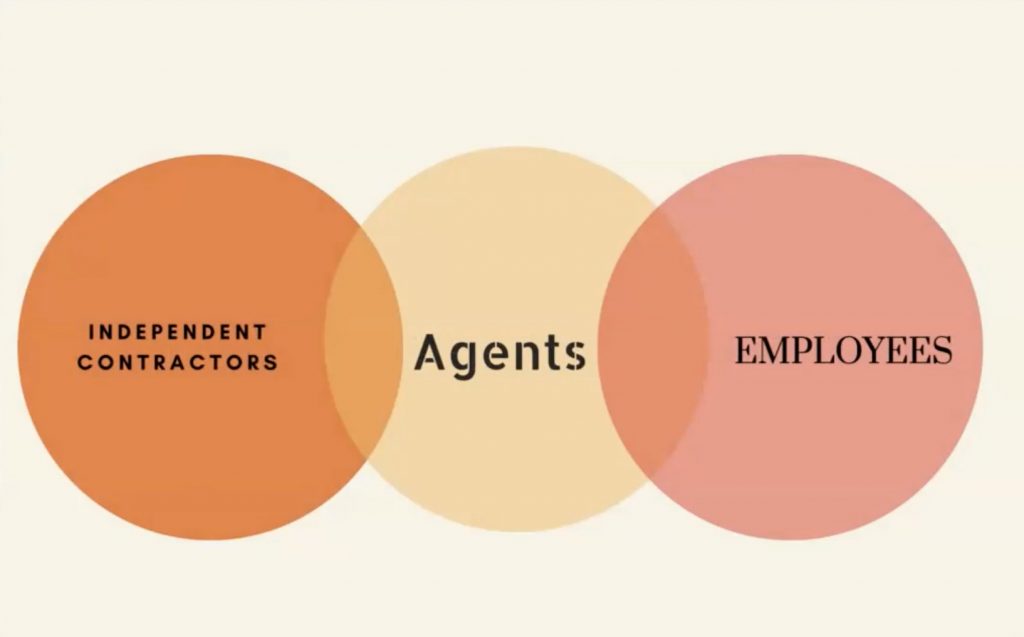
This distinction between employee and independent contractor has important legal consequences for taxation, workers’ compensation, and liability insurance. For example, employers are required to withhold income taxes from their employees’ paychecks. But payment to an independent contractor, such as the plumber for hire, does not require such withholding. Deciding who is an independent contractor is not always easy; there is no single factor or mechanical answer. In Robinson v. New York Commodities Corp., an injured salesman sought workers’ compensation benefits, claiming to be an employee of the New York Commodities Corporation.[2] But the state workmen’s compensation board ruled against him, citing a variety of factors. The claimant sold canned meats, making rounds in his car from his home. The company did not establish hours for him, did not control his movements in any way, and did not reimburse him for mileage or any other expenses or withhold taxes from its straight commission payments to him. He reported his taxes on a form for the self-employed and hired an accountant to prepare it for him. The court agreed with the compensation board that these facts established the salesman’s status as an independent contractor.
The factual situation in each case determines whether a worker is an employee or an independent contractor. Neither the company nor the worker can establish the worker’s status by agreement. As the North Dakota Workmen’s Compensation Bureau put it in a bulletin to real estate brokers, “It has come to the Bureau’s attention that many employers are requiring that those who work for them sign ‘independent contractor’ forms so that the employer does not have to pay workmen’s compensation premiums for his employees. Such forms are meaningless if the worker is in fact an employee.”[3]


Courts may look to various factors such as the amount of control over the work, who provides the tools used to accomplish the work, how the individual is paid, the level of skill taken to complete the work, the duration of the relationship, and so on. There are often not clear answers, as in the continued litigation in the 2010’s over whether Uber drivers are employees or independent contractors. On one hand, Uber controls their work in great detail through the app. On the other hand, the drivers have no obligation to work when they choose not to. The drivers provide the car, which is needed for the job, yet Uber provides the app, without which the drivers cannot find riders. These complexities are far from being completely resolved.
Creating Agency Relationships
Setting aside the question of employee versus independent contract, we return to whether an agency exists. There are three basic ways in which agency power is granted.
Express Authority (Agency Created by Agreement)
The strongest form of authority is that which is expressly granted, often in written form. The principal consents to the agent’s actions, and the third party may then rely on the document attesting to the agent’s authority to deal on behalf of the principal. One common form of express authority is the standard signature card on file with banks allowing corporate agents to write checks on the company’s credit.
This express grant of authority is often part of a contract. In those cases the general rules of contract law covered in Chapter 8 apply. But agencies can also be created without contract, by agreement (for instance, without consideration, which not make the relationship contractual). Therefore, three contract principles are especially important: the first is the requirement for consideration, the second for a writing, and the third concerns contractual capacity.
Consideration
Agencies created by consent—agreement—are not necessarily contractual. It is not uncommon for one person to act as an agent for another without consideration. For example, Abe asks Byron to run some errands for him: to buy some lumber on his account at the local lumberyard. Such a gratuitous agency gives rise to no different results than the more common contractual agency.
Formalities
 Most oral agency contracts are legally binding; the law does not require that they be reduced to writing. In practice, many agency contracts are written to avoid problems of proof. And there are situations where an agency contract must be in writing: (1) if the agreed-on purpose of the agency cannot be fulfilled within one year or if the agency relationship is to last more than one year; (2) in many states, an agreement to pay a commission to a real estate broker; (3) in many states, authority given to an agent to sell real estate; and (4) in several states, contracts between companies and sales representatives.
Most oral agency contracts are legally binding; the law does not require that they be reduced to writing. In practice, many agency contracts are written to avoid problems of proof. And there are situations where an agency contract must be in writing: (1) if the agreed-on purpose of the agency cannot be fulfilled within one year or if the agency relationship is to last more than one year; (2) in many states, an agreement to pay a commission to a real estate broker; (3) in many states, authority given to an agent to sell real estate; and (4) in several states, contracts between companies and sales representatives.
Even when the agency contract is not required to be in writing, contracts that agents make with third parties often must be in writing. Thus Section 2-201 of the Uniform Commercial Code specifically requires contracts for the sale of goods for the price of five hundred dollars or more to be in writing and “signed by the party against whom enforcement is sought or by his authorized agent.”
Capacity
A contract is void or voidable when one of the parties lacks capacity to make one. If both principal and agent lack capacity—for example, a minor appoints another minor to negotiate or sign an agreement—there can be no question of the contract’s voidability. But suppose only one or the other lacks capacity. Generally, the law focuses on the principal. If the principal is a minor or otherwise lacks capacity, the contract can be avoided even if the agent is fully competent. There are, however, a few situations in which the capacity of the agent is important. Thus a mentally incompetent agent cannot bind a principal.
Implied Authority
Implied authority exists to reasonably carry out the express authority granted to the agent. Not every detail of an agent’s work can be spelled out. It is impossible to delineate step-by-step the duties of a general agent; at best, a principal can set forth only the general nature of the duties that the agent is to perform. Even a special agent’s duties are difficult to describe in such detail as to leave him without discretion. If express authority were the only valid kind, there would be no efficient way to use an agent, both because the effort to describe the duties would be too great and because the third party would be reluctant to deal with him.
But the law permits authority to be “implied” by the relationship of the parties, the nature and customs of the business, the circumstances surrounding the act in question, the wording of the agency contract, and the knowledge that the agent has of facts relevant to the assignment. The general rule is that the agent has implied or “incidental” authority to perform acts incidental to or reasonably necessary to carrying out the transaction. Thus if a principal instructs her agent to “deposit a check in the bank today,” the agent has authority to drive to the bank unless the principal specifically prohibits the agent from doing so.

Implied authority is especially important to business in the realm of the business manager, who may be charged with running the entire business operation or only a small part of it. In either event, the business manager has a relatively large domain of implied authority. They can buy goods and services; hire, supervise, and fire employees; sell or junk inventory; take in receipts and pay debts; and in general, direct the ordinary operations of the business. The full extent of the manager’s authority depends on the circumstances—what is customary in the particular industry, in the particular business, and among the individuals directly concerned.
On the other hand, a manager does not have implicit authority to undertake unusual or extraordinary actions on behalf of their principal. In the absence of express permission, an agent may not sell part of the business, start a new business, change the nature of the business, incur debt (unless borrowing is integral to the business, as in banking, for example), or move the business premises. For example, the owner of a hotel appoints Andy manager; Andy decides to rename the hotel and commissions an artist to prepare a new logo for the hotel’s stationery. Andy has no implied authority to change the name or to commission the artist, though he does have implied authority to engage a printer to replenish the stationery supply—and possibly to make some design changes in the letterhead.
Thus, if you are my agent to purchase a buy a house, you could reasonably be expected to have authority to hire a realtor, engage an inspector, and so on. Because of this, implied authority can never contradict express authority! If you are buying a home for me, but I say to never hire a realtor, the action of hiring the realtor would be done without authority, and thus (1) potentially non-binding on the principal and (2) opening the agent up to liability for violating their duty towards the principal.
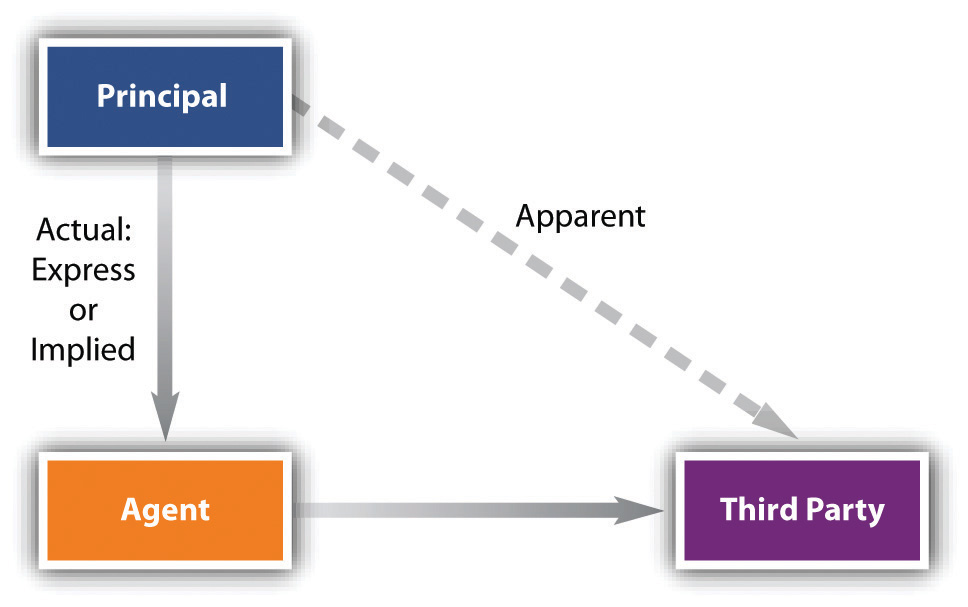
Apparent Authority
In the agency relationship, the agent’s actions in dealing with third parties will affect the legal rights of the principal. What the third party knows about the agency agreement is irrelevant to the agent’s legal authority to act. That authority runs from principal to agent. As long as an agent has authorization, either express or implied, she may bind the principal legally. Thus the seller of a house may be ignorant of the buyer’s true identity; the person they suppose to be the prospective purchaser might be the agent of an undisclosed principal. Nevertheless, if the agent is authorized to make the purchase, the seller’s ignorance is not a ground for either seller or principal to void the deal.
But if a person has no authority to act as an agent, or an agent has no authority to act in a particular way, is the principal free from all consequences? The answer depends on whether or not the agent has apparent authority—that is, on whether or not the third person reasonably believes from the principal’s words, written or spoken, or from their conduct that they have in fact consented to the agent’s actions. Apparent authority is a manifestation of authority communicated to the third person; it runs from principal to third party, not to the agent.

Suppose Arthur is Paul’s agent, employed through October 31. On November 1, Arthur buys materials at Lumber Yard—as he has been doing since early spring—and charges them to Paul’s account. Lumber Yard, not knowing that Arthur’s employment terminated the day before, bills Paul. Will Paul have to pay? Yes, because the termination of the agency was not communicated to Lumber Yard. It appeared that Arthur was an authorized agent.
Key Takeaways
Exercises
- Could express authority be established by silence on the part of the principal?
- Why is the concept of implied authority very important in business situations?
- What is the rationale for the doctrine of apparent authority—that is, why would the law impose a contract on a “principal” when in fact there was no principal-agent relationship with the “agent” at all?
Duties and Liabilities of Principals and Agents
The agent owes the principal duties in two categories: the fiduciary duty and a set of general duties imposed by agency law. But these general duties are not unique to agency law; they are duties owed by any employee to the employer.
Fiduciary Duty
In a nonagency contractual situation, the parties’ responsibilities terminate at the border of the contract. There is no relationship beyond the agreement. This literalist approach is justified by the more general principle that we each should be free to act unless we commit ourselves to a particular course.
But the agency relationship is more than a contractual one, and the agent’s responsibilities go beyond the border of the contract. Agency imposes a higher duty than simply to abide by the contract terms. It imposes a fiduciary duty. The law infiltrates the contract creating the agency relationship and reverses the general principle that the parties are free to act in the absence of agreement. As a fiduciary of the principal, the agent stands in a position of special trust. Their responsibility is to subordinate their self-interest to that of their principal. The fiduciary responsibility is imposed by law. The absence of any clause in the contract detailing the agent’s fiduciary duty does not relieve him of it. The duty contains several aspects: the agent or employee must avoid self-dealing, be loyal, be lawfully obedient, perform their tasks with reasonable skill and care, preserve confidential information, and so on.
The fiduciary duty does not run in reverse: the principal owes the agent general contractual duties but not fiduciary duties. Thus, the principal should, e.g., reimburse the agent for expenses, but does not owe them a duty of loyalty. One particular duty of the employer is to provide workers’ compensation.
Worker’s Compensation
Andy, who works in a dynamite factory, negligently stores dynamite in the wrong shed. Andy warns his fellow employee Bill that he has done so. Bill lights up a cigarette near the shed anyway, a spark lands on the ground, the dynamite explodes, and Bill is injured. May Bill sue his employer to recover damages? At common law, the answer would be no—three times no. First, the “fellow-servant” rule would bar recovery because the employer was held not to be responsible for torts committed by one employee against another. Second, Bill’s failure to heed Andy’s warning and his decision to smoke near the dynamite amounted to contributory negligence. Hence even if the dynamite had been negligently stored by the employer rather than by a fellow employee, the claim would have been dismissed. Third, the courts might have held that Bill had “assumed the risk”: since he was aware of the dangers, it would not be fair to saddle the employer with the burden of Bill’s actions.
The three common-law rules just mentioned ignited intense public fury by the turn of the twentieth century. In large numbers of cases, workers who were mutilated or killed on the job found themselves and their families without recompense. Union pressure and grass roots lobbying led to workers’ compensation acts—statutory enactments that dramatically overhauled the law of torts as it affected employees.
Workers’ compensation is a no-fault system. The employee gives up the right to sue the employer (and, in some states, other employees) and receives in exchange predetermined compensation for a job-related injury, regardless of who caused it. This trade-off was felt to be equitable to employer and employee: the employee loses the right to seek damages for pain and suffering—which can be a sizable portion of any jury award—but in return they can avoid the time-consuming and uncertain judicial process and assure himself that their medical costs and a portion of their salary will be paid—and paid promptly. The employer must pay for all injuries, even those for which they are blameless, but in return they avoid the risk of losing a big lawsuit, can calculate their costs actuarially, and can spread the risks through insurance.
Most workers’ compensation acts provide 100 percent of the cost of a worker’s hospitalization and medical care necessary to cure the injury and relieve him from its effects. They also provide for payment of lost wages and death benefits. Even an employee who is able to work may be eligible to receive compensation for specific injuries.
Although workers’ compensation laws are on the books of every state, in two states—New Jersey and Texas—they are not compulsory. In those states the employer may decline to participate, in which event the employee must seek redress in court. But in those states permitting an employer election, the old common-law defenses (fellow-servant rule, contributory negligence, and assumption of risk) have been statutorily eliminated, greatly enhancing an employee’s chances of winning a suit. The incentive is therefore strong for employers to elect workers’ compensation coverage.
Those frequently excluded are farm and domestic laborers and public employees; public employees, federal workers, and railroad and shipboard workers are covered under different but similar laws. The trend has been to include more and more classes of workers. Approximately half the states now provide coverage for household workers, although the threshold of coverage varies widely from state to state. Some use an earnings test; other states impose an hours threshold. People who fall within the domestic category include maids, baby-sitters, gardeners, and handymen but generally not plumbers, electricians, and other independent contractors.
Recurring legal issues in workers’ compensation include whether the injury was work related, whether the injured person was actually an employee, and whether psychological injury counts.[4]
Liability in Tort
Direct Liability
There is a distinction between torts prompted by the principal himself and torts of which the principal was innocent. If the principal directed the agent to commit a tort or knew that the consequences of the agent’s carrying out their instructions would bring harm to someone, the principal is liable. This is an application of the general common-law principle that one cannot escape liability by delegating an unlawful act to another. The syndicate that hires a hitman is as culpable of murder as the man who pulls the trigger. Similarly, a principal who is negligent in their use of agents will be held liable for their negligence. This rule comes into play when the principal fails to supervise employees adequately, gives faulty directions, or hires incompetent or unsuitable people for a particular job. Imposing liability on the principal in these cases is readily justifiable since it is the principal’s own conduct that is the underlying fault; the principal here is directly liable.
Vicarious Liability
But the principle of liability for one’s agent is much broader, extending to acts of which the principal had no knowledge, that they had no intention to commit nor involvement in, and that they may in fact have expressly prohibited the agent from engaging in. This is the principle of respondeat superior[5] (“let the master answer”) or the master-servant doctrine, which imposes on the principal vicarious liability (vicarious means “indirectly, as, by, or through a substitute”) under which the principal is responsible for acts committed by the agent within the scope of the employment.

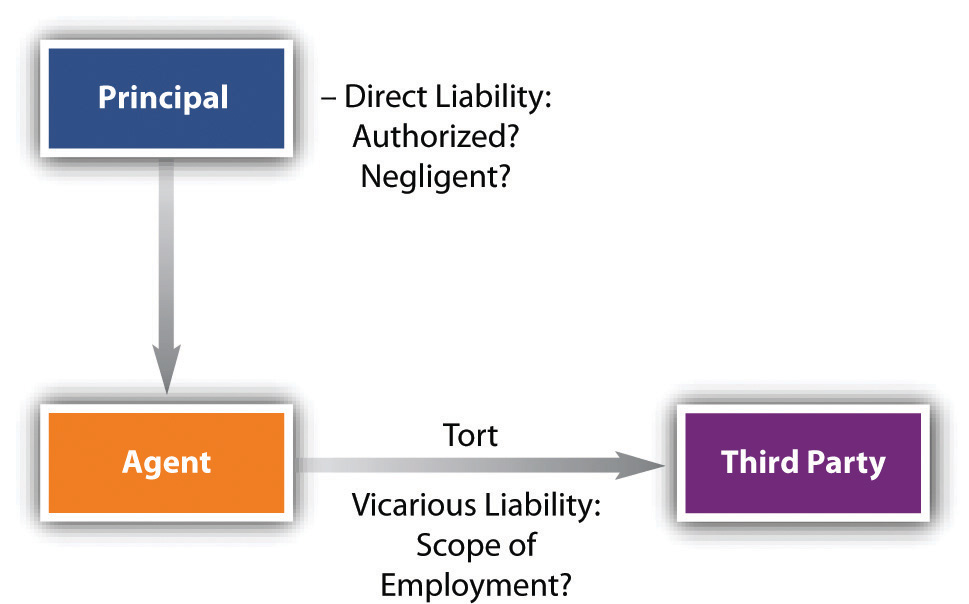
The modern basis for vicarious liability is sometimes termed the “deep pocket” theory: the principal (usually a corporation) has deeper pockets than the agent, meaning that it has the wherewithal to pay for the injuries traceable one way or another to events it set in motion. A million-dollar industrial accident is within the means of a company or its insurer; it is usually not within the means of the agent—employee—who caused it.
In general, the broadest liability is imposed on the master in the case of tortious physical conduct by a servant or employee. If the servant or employee acted within the scope of their employment—that is, if the servant’s wrongful conduct occurred while performing their job—the master will be liable to the victim for damages unless, as we have seen, the victim was another employee, in which event the workers’ compensation system will be invoked. Vicarious tort liability is primarily a function of the employment relationship and not agency status.


Ordinarily, an individual or a company is not vicariously liable for the tortious acts of independent contractors. The plumber who rushes to a client’s house to repair a leak and causes a traffic accident does not subject the homeowner to liability. But there are exceptions to the rule. Generally, these exceptions fall into a category of duties that the law deems nondelegable. In some situations, one person is obligated to provide protection to or care for another. The failure to do so results in liability whether or not the harm befell the other because of an independent contractor’s wrongdoing. Thus a homeowner has a duty to ensure that physical conditions in and around the home are not unreasonably dangerous. If the owner hires an independent contracting firm to dig a sewer line and the contractor negligently fails to guard passersby against the danger of falling into an open trench, the homeowner is liable because the duty of care in this instance cannot be delegated. (The contractor is, of course, liable to the homeowner for any damages paid to an injured passerby.)
Liability for Agent’s Intentional Torts
In the nineteenth century, a principal was rarely held liable for intentional wrongdoing by the agent if the principal did not command the act complained of. The thought was that one could never infer authority to commit a willfully wrongful act. Today, liability for intentional torts is imputed to the principal if the agent is acting to further the principal’s business.
The general rule is that a principal is liable for torts only if the servant committed them “in the scope of employment.” But determining what this means is not easy.
It may be clear that the person causing an injury is the agent of another. But a principal cannot be responsible for every act of an agent. If an employee is following the letter of their instructions, it will be easy to determine liability. But suppose an agent deviates in some way from their job. The classic test of liability was set forth in an 1833 English case, Joel v. Morrison.[6] The plaintiff was run over on a highway by a speeding cart and horse. The driver was the employee of another, and inside was a fellow employee. There was no question that the driver had acted carelessly, but what they and their fellow employee were doing on the road where the plaintiff was injured was disputed. For weeks before and after the accident, the cart had never been driven in the vicinity in which the plaintiff was walking, nor did it have any business there. The suggestion was that the employees might have gone out of their way for their own purposes. As the great English jurist Baron Parke put it, “If the servants, being on their master’s business, took a detour to call upon a friend, the master will be responsible.…But if he was going on a frolic of his own, without being at all on his master’s business, the master will not be liable.” In applying this test, the court held the employer liable.

The test is thus one of degree, and it is not always easy to decide when a detour has become so great as to be transformed into a frolic. For a time, a rather mechanical rule was invoked to aid in making the decision. The courts looked to the servant’s purposes in “detouring.” If the servant’s mind was fixed on accomplishing their own purposes, then the detour was held to be outside the scope of employment; hence the tort was not imputed to the master. But if the servant also intended to accomplish their master’s purposes during their departure from the letter of their assignment, or if they committed the wrong while returning to their master’s task after the completion of their frolic, then the tort was held to be within the scope of employment.
This test is not always easy to apply. If a hungry delivery driver stops at a restaurant outside the normal lunch hour, intending to continue to their next delivery after eating, they are within the scope of employment. But suppose they decide to take the truck home that evening, in violation of rules, in order to get an early start the next morning. Suppose they decide to stop by the beach, which is far away from the route. Does it make a difference if the employer knows that the driver do this?
Court decisions in the last forty years have moved toward a different standard, one that looks to the foreseeability of the agent’s conduct. By this standard, an employer may be held liable for their employee’s conduct even when devoted entirely to the employee’s own purposes, as long as it was foreseeable that the agent might act as he did. This is the “zone of risk” test. The employer will be within the zone of risk for vicarious liability if the employee is where she is supposed to be, doing—more or less—what she is supposed to be doing, and the incident arose from the employee’s pursuit of the employer’s interest (again, more or less). That is, the employer is within the zone of risk if the servant is in the place within which, if the master were to send out a search party to find a missing employee, it would be reasonable to look.
Liability in Contract
The key to determining whether a principal is liable for contracts made by their agent is authority: was the agent authorized to negotiate the agreement and close the deal? Obviously, it would not be sensible to hold a contractor liable to pay for a whole load of lumber merely because a stranger wandered into the lumberyard saying, “I’m an agent for ABC Contractors; charge this to their account.” To be liable, the principal must have authorized the agent in some manner to act in their behalf, and that authorization must be communicated to the third party by the principal.
The agent will be liable in some cases as well. If the agent acted without authority, then they weren’t really acting as an agent and so will be personally liable for their contractual actions. If the third-party does not know the agent is acting for a principal (that is, if the principal is undisclosed), the third party will naturally sue the agent.[7] For these reasons, agents who wish to avoid liability should always make it clear they are acting as agent for someone else. For example, an agent acting for a corporation in signing documents might wish their signature block to read “Jane Doe, Agent for BigCorp” or something similar. Finally, an agent acting in their personal capacity remains liable for their personal contracts!
Ratification
Even if the agent possessed no actual authority and there was no apparent authority on which the third person could rely, the principal may still be liable if they ratify or adopt the agent’s acts before the third person withdraws from the contract. Ratification usually relates back to the time of the undertaking, creating authority after the fact as though it had been established initially. Ratification is a voluntary act by the principal. Faced with the results of action purportedly done on their behalf but without authorization and through no fault of their own, they may affirm or disavow them as they choose. To ratify, the principal may tell the parties concerned or by their conduct manifest that they are willing to accept the results as though the act were authorized. Or by their silence they may find under certain circumstances that they have ratified. Note that ratification does not require the usual consideration of contract law. The principal need be promised nothing extra for their decision to affirm to be binding. Nor does ratification depend on the position of the third party; for example, a loss stemming from their reliance on the agent’s representations is not required. In most situations, ratification leaves the parties where they expected to be, correcting the agent’s errors harmlessly and giving each party what was expected.
Key Takeaways
The principal is liable on an agent’s contract only if the agent was authorized by the principal to make the contract. Apparent authority counts!
The principal will be liable for the employee’s torts in two circumstances: first, if the principal was directly responsible, as in hiring a person the principal knew or should have known was incompetent or dangerous; second, if the employee committed the tort in the scope of business for the principal. This is the master-servant doctrine or respondeat superior. It imposes vicarious liability on the employer: the master (employer) will be liable if the employee was in the zone of activity creating a risk for the employer (“zone of risk” test), that is—generally—if the employee was where there were supposed to be, when they were supposed to be there, and the incident arose out of the employee’s interest (however perverted) in promoting the employer’s business.
Exercises
- What is the difference between direct and vicarious employer tort liability?
- What is meant by the “zone of risk” test?
- Under what circumstances will an employer be liable for intentional torts of the employee?
Employment at Will
The basis of employment law in the United States is employment at will: that is, at common law, an employee without a contract guaranteeing a job for a specific period was an employee at will and could be fired at any time and for any reason, or even for no reason at all. Various federal statutes we will examine have made inroads on the at-will doctrine, but the foundational principle of American employment law remains, with modern caveats.
The courts and legislatures in more than forty states have made revolutionary changes in the at-will doctrine. They have done so under three theories: tort, contract, and duty of good faith and fair dealing. We will first consider the tort of wrongful discharge.
Courts have created a major exception to the employment-at-will rule by allowing the tort of wrongful discharge. Wrongful discharge means firing a worker for a bad reason. What is a bad reason? A bad reason can be (1) discharging an employee for refusing to violate a law, (2) discharging an employee for exercising a legal right, (3) discharging an employee for performing a legal duty, and (4) discharging an employee in a way that violates public policy.
Discharging an Employee for Refusing to Violate a Law
Some employers will not want employees to testify truthfully at trial. In one case, a nurse refused a doctor’s order to administer a certain anesthetic when she believed it was wrong for that particular patient; the doctor, angry at the nurse for refusing to obey him, then administered the anesthetic himself. The patient soon stopped breathing. The doctor and others could not resuscitate him soon enough, and he suffered permanent brain damage. When the patient’s family sued the hospital, the hospital told the nurse she would be in trouble if she testified. She did testify according to her oath in the court of law (i.e., truthfully), and after several months of harassment, was finally fired on a pretext. The hospital was held liable for the tort of wrongful discharge. As a general rule, you should not fire an employee for refusing to break the law.
Discharging an Employee for Exercising a Legal Right
Suppose Bob Berkowitz files a claim for workers’ compensation for an accident at Pacific Gas & Electric, where he works and where the accident that injured him took place. He is fired for doing so, because the employer does not want to have its workers’ comp premiums increased. In this case, the right exercised by Berkowitz is supported by public policy: he has a legal right to file the claim, and if he can establish that their discharge was caused by their filing the claim, he will prove the tort of wrongful discharge.
Discharging an Employee for Performing a Legal Duty
Courts have long held that an employee may not be fired for serving on a jury. This is so even though courts do recognize that many employers have difficulty replacing employees called for jury duty. Jury duty is an important civic obligation, and employers are not permitted to undermine it.
Discharging an Employee in a Way That Violates Public Policy
This is probably the most controversial basis for a tort of wrongful discharge. There is an inherent vagueness in the phrase “basic social rights, duties, or responsibilities.” This is similar to the exception in contract law: the courts will not enforce contract provisions that violate public policy. (For the most part, public policy is found in statutes and in cases.) But what constitutes public policy is an important decision for state courts. In Wagenseller v. Scottsdale Memorial Hospital,[8] for example, a nurse who refused to “play along” with her coworkers on a rafting trip was discharged. The group of coworkers had socialized at night, drinking alcohol; when the partying was near its peak, the plaintiff refused to be part of a group that performed nude actions to the tune of “Moon River” (a composition by Henry Mancini that was popular in the 1970s). The court, at great length, considered that “mooning” was a misdemeanor under Arizona law and that therefore her employer could not discharge her for refusing to violate a state law.
Contract Modification of Employment at Will
Contract law can modify employment at will. Oral promises made in the hiring process may be enforceable even though the promises are not approved by top management. Employee handbooks may create implied contracts that specify personnel processes and statements that the employees can be fired only for a “just cause” or only after various warnings, notice, hearing, or other procedures.
Good Faith and Fair Dealing Standard
A few states, among them Massachusetts and California, have modified the at-will doctrine in a far-reaching way by holding that every employer has entered into an implied covenant of good faith and fair dealing with its employees. That means, the courts in these states say, that it is “bad faith” and therefore unlawful to discharge employees to avoid paying commissions or pensions due them. Under this implied covenant of fair dealing, any discharge without good cause—such as incompetence, corruption, or habitual tardiness—is actionable. This is not the majority view.
Key Takeaways
Although employment at will is still the law, numerous exceptions have been established by judicial decision. Employers can be liable for the tort of wrongful discharge if they discharge an employee for refusing to violate a law, for exercising a legal right or performing a legal duty, or in a way that violates basic public policy.
Exercises
- Richard Mudd, an employee of Compuserve, is called for jury duty in Wayne County, Michigan. His immediate supervisor, Harvey Lorie, lets him know that he “must” avoid jury duty at all costs. Mudd tells the judge of his circumstances and his need to be at work, but the judge refuses to let Mudd avoid jury duty. Mudd spends the next two weeks at trial. He sends regular e-mails and texts to Lorie during this time, but on the fourth day gets a text message from Lorie that says, “Don’t bother to come back.” When he does return, Lorie tells him he is fired. Does Mudd have a cause of action for the tort of wrongful discharge?
- Olga Monge was a schoolteacher in her native Costa Rica. She moved to New Hampshire and attended college in the evenings to earn US teaching credentials. At night, she worked at the Beebe Rubber Company after caring for her husband and three children during the day. When she applied for a better job at the plant, the foreman offered to promote her if she would be “nice” and go out on a date with him. She refused, and he assigned her to a lower-wage job, took away her overtime, made her clean the washrooms, and generally ridiculed her. She finally collapsed at work, and he fired her. Does Monge have any cause of action?
Federal Employment Discrimination Laws
Perhaps the most well-known modification of the common law of employment in the United States are federal anti-discrimination laws such as Title VII. As we look at federal employment discrimination laws, bear in mind that most states also have laws that prohibit various kinds of discriminatory practices in employment. Until the 1960s, Congress had intruded but little in the affairs of employers except in union relationships. A company could refuse to hire members of racial minorities, exclude women from promotions, or pay men more than women for the same work. But with the rise of the civil rights movement in the early 1960s, Congress (and many states) began to legislate away the employer’s frequently exercised power to discriminate. The most important statutes are Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, the Equal Pay Act of 1963, the Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 1967, and the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990.
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964


The most basic anti-discrimination law in employment is in Title VII of the federal Civil Rights Act of 1964. In Title VII, Congress for the first time outlawed discrimination in employment based on race, religion, sex, or national origin:. Title VII declares: “It shall be an unlawful employment practice for an employer to fail or refuse to hire or to discharge any individual, or otherwise to discriminate against any individual with respect to his compensation, terms, conditions, or privileges of employment, because of such individual’s race, color, religion, sex, or national origin.” Title VII applies to (1) employers with fifteen or more employees whose business affects interstate commerce, (2) all employment agencies, (3) labor unions with fifteen or more members, (4) state and local governments and their agencies, and (5) most federal government employment.[9]
Title VII established the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) to investigate violations of the act. A victim of discrimination who wishes to file suit must first file a complaint with the EEOC to permit that agency to attempt conciliation of the dispute. The EEOC has filed a number of lawsuits to prove statistically that a company has systematically discriminated on one of the forbidden bases. The EEOC has received perennial criticism for its extreme slowness in filing suits and for failure to handle the huge backlog of complaints with which it has had to wrestle.
The courts have come to recognize two major types of Title VII cases:
(1) Disparate Treatment
In this type of lawsuit, the plaintiff asserts that because of race, sex, religion, or national origin, they have been treated less favorably than others within the organization. To prevail in a disparate treatment suit, the plaintiff must show that the company intended to discriminate because of one of the factors the law forbids to be considered. Thus in McDonnell Douglas Corp. v. Green, the Supreme Court held that the plaintiff had shown that the company intended to discriminate by refusing to rehire him because of his race.[10] Based on that case, courts use a burden-shifting framework to evaluate Title VII cases.
- First, the plaintiff needs to allege membership in a protected class and that they suffered an adverse action. An adverse action could include not being hired, being fired, being passed over for a promotion or a raise, or so on.
- If the plaintiff can make this showing, the burden shifts to the defendant to show a legitimate, non-discriminatory reason for the action. These will be discussed later under “Defenses to Employment Discrimination”.
- Finally, if the defendant can show a legitimate reason for the action, the burden shifts back to the plaintiff to show “pretext”, that is, to show that the real reason for the action was discriminatory.
(2) Disparate Impact
In this second type of Title VII case, the employee need not show that the employer intended to discriminate but only that the effect, or impact, of the employer’s action was discriminatory. Usually, this impact will be upon an entire class of employees. The plaintiff must demonstrate that the reason for the employer’s conduct (such as refusal to promote) was not job related. Disparate impact cases often arise out of practices that appear to be neutral or nondiscriminatory on the surface, such as educational requirements and tests administered to help the employer choose the most qualified candidate. In the seminal case of Griggs v. Duke Power Co., the Supreme Court held that under Title VII, an employer is not free to use any test it pleases; the test must bear a genuine relationship to job performance.[11] Griggs stands for the proposition that Title VII “prohibits employment practices that have discriminatory effects as well as those that are intended to discriminate.”
The same burden shifting framework applies, with some difference. For example, if an employer is using a neutral test to screen applicants, the plaintiff’s prima facie case can be built on statistical evidence showing that, e.g., all women passed the test but half of men did not, or vice versa. The employer would then show a legitimate business reason for the test, after which the burden would shift to the plaintiff to show that a less discriminatory test that accomplished that interest exists.


We now cover several specific areas of discrimination.
Discrimination Based on Religion
An employer who systematically refuses to hire Catholics, Jews, Buddhists, or members of any other religious group engages in unlawful disparate treatment under Title VII. But refusal to deal with someone because of their religion is not the only type of violation under the law. Title VII defines religion as including religious observances and practices as well as belief and requires the employer to “reasonably accommodate to an employee’s or prospective employee’s religious observance or practice” unless the employer can demonstrate that a reasonable accommodation would work an “undue hardship on the conduct of the employer’s business.” Thus a company that refused even to consider permitting a devout Sikh to wear his religiously prescribed turban on the job would violate Title VII.

 But the company need not make an accommodation that would impose more than a minimal cost. For example, an employee in an airline maintenance department, open twenty-four hours a day, wished to avoid working on his Sabbath. The employee belonged to a union, and under the collective bargaining agreement, a rotation system determined by seniority would have put the worker into a work shift that fell on his Sabbath. The Supreme Court held that the employer was not required to pay premium wages to someone whom the seniority system would not require to work on that day and could discharge the employee if they refused the assignment.
But the company need not make an accommodation that would impose more than a minimal cost. For example, an employee in an airline maintenance department, open twenty-four hours a day, wished to avoid working on his Sabbath. The employee belonged to a union, and under the collective bargaining agreement, a rotation system determined by seniority would have put the worker into a work shift that fell on his Sabbath. The Supreme Court held that the employer was not required to pay premium wages to someone whom the seniority system would not require to work on that day and could discharge the employee if they refused the assignment.
Sex Discrimination
A refusal to hire or promote a woman simply because she is female is a clear violation of Title VII. Under the Pregnancy Act of 1978, Congress declared that discrimination because of pregnancy is a form of sex discrimination. Equal pay for equal or comparable work has also been an issue in sex (or gender) discrimination.
The late 1970s brought another problem of sex discrimination to the fore: sexual harassment. There is much fear and ignorance about sexual harassment among both employers and employees. Many men think they cannot compliment a woman on her appearance without risking at least a warning by the human resources department. Many employers have spent significant time and money trying to train employees about sexual harassment, so as to avoid lawsuits. Put simply, sexual harassment involves unwelcome sexual advances, requests for sexual favors, and other verbal or physical conduct of a sexual nature.
There are two major categories of sexual harassment: (1) quid pro quo and (2) hostile work environment.
Quid pro quo harassment
Quid pro quo comes from the Latin phrase “one thing in return for another.” If any part of a job is made conditional on sexual activity, there is quid pro quo sexual harassment. Here, one person’s power over another is essential; a coworker, for example, is not usually in a position to make sexual demands on someone at their same level, unless they have special influence with a supervisor who has power to hire, fire, promote, or change work assignments. A supervisor, on the other hand, typically has those powers or the power to influence those kinds of changes. For example, when the male foreman says to the female line worker, “I can get you off of the night shift if you’ll sleep with me,” there is quid pro quo sexual harassment
Hostile work environment
Hostile work environment claims are more frequent than quid pro quo claims and so are more worrisome to management. An employee has a valid claim of sexual harassment if sexual talk, imagery, or behavior becomes so pervasive that it interferes with the employee’s ability to work to her best capacity. On occasion, courts have found that offensive jokes, if sufficiently frequent and pervasive in the workplace, can create a hostile work environment. Likewise, comments about body parts or public displays of pornographic pictures can also create a hostile work environment. In short, the plaintiff can be detrimentally offended and hindered in the workplace even if there are no measurable psychological injuries.
Discrimination Based on Race, Color, and National Origin
Title VII was primarily enacted to prohibit employment discrimination based on race, color, and national origin. Race refers to broad categories such as black, Caucasian, Asian, and Native American. Color simply refers to the color of a person’s skin, and national origin refers to the country of the person’s ancestry.
Discrimination based on sexual orientation
In 2020, the Supreme Court decided Bostock v. Clayton County. In that case, the Court found that discrimination based on sexual orientation was discrimination based on sex, and thus actionable under Title VII. The Court’s reasoning is worth noting, as it focuses on the text of the law over the “anticipation” of the drafters:
Sometimes small gestures can have unexpected consequences. Major initiatives practically guarantee them. In our time, few pieces of federal legislation rank in significance with the Civil Rights Act of 1964. There, in Title VII, Congress outlawed discrimination in the workplace on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, or national origin. Today, we must decide whether an employer can fire someone simply for being homosexual or transgender. The answer is clear. An employer who fires an individual for being homosexual or transgender fires that person for traits or actions it would not have questioned in members of a different sex. Sex plays a necessary and undisguisable role in the decision, exactly what Title VII forbids.
Those who adopted the Civil Rights Act might not have anticipated their work would lead to this particular result. Likely, they weren’t thinking about many of the Act’s consequences that have become apparent over the years, including its prohibition against discrimination on the basis of motherhood or its ban on the sexual harassment of male employees. But the limits of the drafters’ imagination supply no reason to ignore the law’s demands. When the express terms of a statute give us one answer and extratextual considerations suggest another, it’s no contest. Only the written word is the law, and all persons are entitled to its benefit.
Defenses to Employment Discrimination
Merit
Employers are allowed to select on merit and promote on merit without offending title VII’s requirements. Merit decisions are usually based on work, educational experience, and ability tests. All requirements, however, must be job related. For example, the ability to lift heavy cartons of sixty pounds or more is appropriate for certain warehouse jobs but is not appropriate for all office workers. The ability to do routine maintenance (electrical, plumbing, construction) is an appropriate requirement for maintenance work but not for a teaching position.
Seniority
Employers may also maintain seniority systems that reward workers who have been with the company for a long time. Higher wages, benefits, and choice of working hours or vacation schedules are examples of rewards that provide employees with an incentive to stay with the company. If they are not the result of intentional discrimination, they are lawful. Where an employer is dealing with a union, it is typical to see seniority systems in place.
Bona Fide Occupational Qualification (BFOQ)
For certain kinds of jobs, employers may impose bona fide occupational qualifications (BFOQs). Under the express terms of Title VII, however, a bona fide (good faith) occupational qualification of race or color is never allowed. In the area of religion, as noted earlier, a group of a certain religious faith that is searching for a new spiritual leader can certainly limit its search to those of the same religion. With regard to sex (gender), allowing women to be locker-room attendants only in a women’s gym is a valid BFOQ. One important test that the courts employ in evaluating an employer’s BFOQ claims is the “essence of the business” test.
Defenses in Sexual Harassment Cases
The Supreme Court has rejected the notion of strict or automatic liability for employers when agents (employees) engage in sexual harassment. But the employer can have a valid defense to liability if it can prove (1) that it exercised reasonable care to prevent and correct any sexual harassment behaviors and (2) that the plaintiff employee unreasonably failed to take advantage of any preventive or corrective opportunities provided by the employer or to otherwise avoid harm. As with all affirmative defenses, the employer has the burden of proving this defense.
Other Employment-Related Laws
The Age Discrimination in Employment Act
The Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA) of 1967 (amended in 1978 and again in 1986) prohibits discrimination based on age, and recourse to this law has been growing at a faster rate than any other federal antibias employment law. In particular, the act protects workers over forty years of age and prohibits forced retirement in most jobs because of age. Until 1987, federal law had permitted mandatory retirement at age seventy, but the 1986 amendments that took effect January 1, 1987, abolished the age ceiling except for a few jobs, such as firefighters, police officers, tenured university professors, and executives with annual pensions exceeding $44,000. Like Title VII, the law has a BFOQ exception—for example, employers may set reasonable age limitations on certain high-stress jobs requiring peak physical condition.
Disabilities: Discrimination against the Handicapped
The 1990 Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) prohibits employers from discriminating on the basis of disability. A disabled person is someone with a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits a major life activity or someone who is regarded as having such an impairment. This definition includes people with mental illness, epilepsy, visual impairment, dyslexia, and AIDS. It also covers anyone who has recovered from alcoholism or drug addiction. It specifically does not cover people with sexual disorders, pyromania, kleptomania, exhibitionism, or compulsive gambling.
Employers cannot disqualify an employee or job applicant because of disability as long as they can perform the essential functions of the job, with reasonable accommodation. Reasonable accommodation might include installing ramps for a wheelchair, establishing more flexible working hours, creating or modifying job assignments, and the like.
Reasonable accommodation means that there is no undue hardship for the employer. The law does not offer uniform standards for identifying what may be an undue hardship other than the imposition on the employer of a “significant difficulty or expense.” Cases will differ: the resources and situation of each particular employer relative to the cost or difficulty of providing the accommodation will be considered; relative cost, rather than some definite dollar amount, will be the issue.
Equal Pay Act
The Equal Pay Act of 1963 protects both men and women from pay discrimination based on sex. The act covers all levels of private sector employees and state and local government employees but not federal workers. The act prohibits disparity in pay for jobs that require equal skill and equal effort. Equal skill means equal experience, and equal effort means comparable mental and/or physical exertion. The act prohibits disparity in pay for jobs that require equal responsibility, such as equal supervision and accountability, or similar working conditions.
In making their determinations, courts will look at the stated requirements of a job as well as the actual requirements of the job. If two jobs are judged to be equal and similar, the employer cannot pay disparate wages to members of different sexes. Along with the EEOC enforcement, employees can also bring private causes of action against an employer for violating this act. There are four criteria that can be used as defenses in justifying differentials in wages: seniority, merit, quantity or quality of product, and any factor other than sex. The employer will bear the burden of proving any of these defenses.
Occupational Safety and Health Act
In a heavily industrialized society, workplace safety is a major concern. Hundreds of studies for more than a century have documented the gruesome toll taken by hazardous working conditions in mines, on railroads, and in factories from tools, machines, treacherous surroundings, and toxic chemicals and other substances. Studies in the late 1960s showed that more than 14,000 workers were killed and 2.2 million were disabled annually—at a cost of more than $8 billion and a loss of more than 250 million worker days. Congress responded in 1970 with the Occupational Safety and Health Act, the primary aim of which is “to assure so far as possible every working man and woman in the Nation safe and healthful working conditions.”


The act imposes on each employer a general duty to furnish a place of employment free from recognized hazards likely to cause death or serious physical harm to employees. It also gives the secretary of labor the power to establish national health and safety standards. The standard-making power has been delegated to the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), an agency within the US Department of Labor. The agency has the authority to inspect workplaces covered by the act whenever it receives complaints from employees or reports about fatal or multiple injuries. The agency may assess penalties and proceed administratively to enforce its standards. Criminal provisions of the act are enforced by the Justice Department.
During its first two decades, OSHA was criticized for not issuing standards very quickly: fewer than thirty national workplace safety standards were issued by 1990. But not all safety enforcement is in the hands of the federal government: although OSHA standards preempt similar state standards, under the act the secretary may permit the states to come up with standards equal to or better than federal standards and may make grants to the states to cover half the costs of enforcement of the state safety standards.
Employee Retirement Income Security Act
More than half the US workforce is covered by private pension plans for retirement. One 1988 estimate put the total held in pension funds at more than $1 trillion, costing the federal Treasury nearly $60 billion annually in tax write-offs. As the size of the private pension funds increased dramatically in the 1960s, Congress began to hear shocking stories of employees defrauded out of pension benefits, deprived of a lifetime’s savings through various ruses (e.g., by long vesting provisions and by discharges just before retirement). To put an end to such abuses, Congress, in 1974, enacted the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA).
In general, ERISA governs the vesting of employees’ pension rights and the funding of pension plans. Within five years of beginning employment, employees are entitled to vested interests in retirement benefits contributed on their behalf by individual employers. Multiemployer pension plans must vest their employees’ interests within ten years. A variety of pension plans must be insured through a federal agency, the Pension Benefit Guaranty Corporation, to which employers must pay annual premiums. The corporation may assume financial control of underfunded plans and may sue to require employers to make up deficiencies. The act also requires pension funds to disclose financial information to beneficiaries, permits employees to sue for benefits, governs the standards of conduct of fund administrators, and forbids employers from denying employees their rights to pensions. The act largely preempts state law governing employee benefits.
Fair Labor Standards Act
In the midst of the Depression, Congress enacted at President Roosevelt’s urging a national minimum wage law, the Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 (FLSA). The act prohibits most forms of child labor and established a scale of minimum wages for the regular workweek and a higher scale for overtime. (The original hourly minimum was twenty-five cents, although the administrator of the Wage and Hour Division of the US Department of Labor, a position created by the act, could raise the minimum rate industry by industry.) The act originally was limited to certain types of work: that which was performed in transporting goods in interstate commerce or in producing goods for shipment in interstate commerce.
Employers quickly learned that they could limit the minimum wage by, for example, separating the interstate and intrastate components of their production. Within the next quarter century, the scope of the FLSA was considerably broadened, so that it now covers all workers in businesses that do a particular dollar-volume of goods that move in interstate commerce, regardless of whether a particular employee actually works in the interstate component of the business. It now covers between 80 and 90 percent of all persons privately employed outside of agriculture, and a lesser but substantial percentage of agricultural workers and state and local government employees. Violations of the act are investigated by the administrator of the Wage and Hour Division, who has authority to negotiate back pay on the employee’s behalf. If no settlement is reached, the Labor Department may sue on the employee’s behalf, or the employee, armed with a notice of the administrator’s calculations of back wages due, may sue in federal or state court for back pay. Under the FLSA, a successful employee will receive double the amount of back wages due.
Key Takeaways
Starting with employment at will as a common-law doctrine, we see many modifications by statute, particularly after 1960. Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 is the most significant, for it prohibits employers engaged in interstate commerce from discriminating on the basis of race, color, sex, religion, or national origin.
Sex discrimination, especially sexual harassment, has been a particularly fertile source of litigation. There are many defenses to Title VII claims: the employer may have a merit system or a seniority system in place, or there may be bona fide occupational qualifications in religion, gender, or national origin. In addition to Title VII, federal statutes limiting employment discrimination are the ADEA, the ADA, and the Equal Pay Act. Other significant federal laws include OSHA and the FLSA.
Exercises
- Go to the EEOC website. Describe the process by which an employee or ex-employee who wants to make a Title VII claim obtains a right-to-sue letter from the EEOC.
- Again, looking at the EEOC website, find the statistical analysis of Title VII claims brought to the EEOC. What kind of discrimination is most frequent?
- According to the EEOC website, what is “retaliation”? How frequent are retaliation claims relative to other kinds of claims?
- Greg Connolly is a member of the Church of God and believes that premarital sex and abortion are sinful. He works as a pharmacist for Wal-Mart, and at many times during the week, he is the only pharmacist available to fill prescriptions. One product sold at his Wal-Mart is the morning-after pill (RU 468). Based on his religious beliefs, he tells his employer that he will refuse to fill prescriptions for the morning-after pill. Must Wal-Mart make a reasonable accommodation to his religious beliefs?
Summary
An agent is one who acts on behalf of another. The law recognizes several types of agents, including (1) the general agent, one who possesses authority to carry out a broad range of transactions in the name of and on behalf of the principal; (2) the special agent, one with authority to act only in a specifically designated instance or set of transactions; (3) the agent whose agency is coupled with an interest, one who has a property interest in addition to authority to act as an agent; (4) the subagent, one appointed by an agent with authority to do so; and (5) the servant (“employee” in modern English), one whose physical conduct is subject to control of the principal.
A servant should be distinguished from an independent contractor, whose work is not subject to the control of the principal. The difference is important for purposes of taxation, workers’ compensation, and liability insurance.
A contract made by an agent on behalf of the principal legally binds the principal. Three types of authority may bind the principal: (1) express authority—that which is actually given and spelled out, (2) implied authority—that which may fairly be inferred from the parties’ relationship and which is incidental to the agent’s express authority, and (3) apparent authority—that which reasonably appears to a third party under the circumstances to have been given by the principal. Even in the absence of authority, a principal may ratify the agent’s acts.
The principal may be liable for tortious acts of the agent but except under certain regulatory statutes may not be held criminally liable for criminal acts of agents not prompted by the principal. Under the doctrine of respondeat superior, a principal is generally liable for acts by a servant within the scope of employment. What constitutes scope of employment is not easy to determine; the modern trend is to hold a principal liable for the conduct of an agent if it was foreseeable that the agent might act as he did.
At common law, an employer was free to fire an employee for any reason or for no reason at all. In recent years, the employment-at-will doctrine has been seriously eroded. Many state courts have found against employers on the basis of implied contracts, tortious violation of public policy, or violations of an implied covenant of good faith and fair dealing.
For the past forty-eight years, Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 has prohibited employment discrimination based on race, religion, sex, or national origin. In 2020, the Supreme Court interpreted this law to prohibit employment discrimination based on sexual orientation. Any employment decision, including hiring, promotion, and discharge, based on one of these factors is unlawful and subjects the employer to an award of back pay, promotion, or reinstatement. The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) may file suits, as may the employee—after the commission screens the complaint.
Exercises
- Parke-Bernet Galleries, acting as agent for an undisclosed principal, sold a painting to Weisz. Weisz later discovered that the painting was a forgery and sued Parke-Bernet for breach of contract. In defense, Parke-Bernet argued that as a general rule, agents are not liable on contracts made for principals. Is this a good defense? Explain.
- Lynch was the loan officer at First Bank. Patterson applied to borrow $25,000. Bank policy required that Lynch obtain a loan guaranty from Patterson’s employer, a milk company. The manager of the milk company visited the bank and signed a guaranty on behalf of the company. The last paragraph of the guaranty stated, “This guaranty is signed by an officer having legal right to bind the company through authorization of the Board of Directors.” Should Lynch be satisfied with this guaranty? Would he be satisfied if the president of the milk company, who was also a director, affirmed that the manager had authority to sign the guaranty? Explain.
- A guest arrived early one morning at the Hotel Ohio. Clemens, a person in the hotel office who appeared to be in charge, walked behind the counter, registered the guest, gave him a key, and took him to his room. The guest also checked valuables (a diamond pin and money) with Clemens, who signed a receipt on behalf of the hotel. Clemens in fact was a roomer at the hotel, not an employee, and had no authority to act on behalf of the hotel. When Clemens absconded with the valuables, the guest sued the hotel. Is the hotel liable? Why?
- A doctor in a University of Chicago hospital seriously assaulted a patient in an examining room. The patient sued the hospital on the theory that the doctor was an agent or employee of the hospital and the assault occurred within the hospital. Is the hospital liable for the acts of its agent? Why?
- In the past decades organizations such as the Catholic Church and the Boy Scouts of America have paid out hundreds of millions of dollars in damage awards to people—mostly men—who claimed that when they were boys and teenagers they were sexually abused by their local parish priests or leaders, often on Church or Scout premises. Obviously, such behavior is antithetical to any reasonable standard of clergy or scouting behavior: the priests could not have been in the scope of employment, and the Scout leaders are often not employees at all. How are these organizations held liable?
- Rainbow Airlines, a new air carrier headquartered in Chicago with routes from Rome to Canberra, extensively studied the psychology of passengers and determined that more than 93 percent of its passengers felt most comfortable with female flight attendants between the ages of twenty-one and thirty-four. To increase its profitability, the company issued a policy of hiring only such people for jobs in the air but opened all ground jobs to anyone who could otherwise qualify. The policy made no racial distinction, and, in fact, nearly 30 percent of the flight attendants hired were black. What violations of federal law has Rainbow committed, if any?
- Ernest lost both his legs in combat in Vietnam. He has applied for a job with Excelsior Products in the company’s quality control lab. The job requires inspectors to randomly check products coming off the assembly line for defects. Historically, all inspectors have stood two-hour shifts. Ernest proposes to sit in his wheelchair. The company refuses to hire him because it says he will be less efficient. Ernest’s previous employment record shows him to be a diligent, serious worker. Does Ernest have a legal right to be hired? What additional facts might you want to know in deciding?
- Flick v. Crouch, 434 P.2d 256, 260 (OK, 1967). Because these lines are not clear, we will limit our analysis to whether there is an agency or not, and whether someone acts as an employee or independent contractor, rather than examining when and in what sense an independent contractor acts as an agent. ↵
- Robinson v. New York Commodities Corp., 396 N.Y.S.2d 725, App. Div. (1977). ↵
- Vizcaino v. Microsoft Corporation. ↵
- Most courts now recognize psychological trauma as injury. ↵
- The Latin term for the master-servant doctrine. ↵
- Joel v. Morrison, 6 Carrington & Payne 501. ↵
- The principal would then have the responsibility to indemnify the agent. If the third party knows a principal is involved but not their identity, this is called a "partially disclosed" principal and a similar rule applies. ↵
- Wagenseller v. Scottsdale Memorial Hospital, 147 Ariz. 370; 710 P.2d 1025 (1085). ↵
- In 1984, the Supreme Court said that Title VII applies to partnerships as well as corporations when ruling that it is illegal to discriminatorily refuse to promote a female lawyer to partnership status in a law firm. This applies, by implication, to other fields, such as accounting. ↵
- McDonnell Douglas Corp. v. Green, 411 U.S. 792 (1973). ↵
- Griggs v. Duke Power Co., 401 U.S. 424 (1971). ↵
Someone authorized to transact every kind of business for the principal.
An agent hired by contract to carry out specifically stated activities.
An agency in which the agent has an interest in the property regarding which he or she is acting on the principal’s behalf.
A person who is hired to accomplish a result but is not subject to specific control by the one hiring.
Contractually given authority to the agent from the principal, orally or in writing, communicated to the third party.
An agency where the agent receives no compensation.
In agency, the situation in which a principal leads a third party to believe that an agent has authority to bind the principal, even where the agent lacks the actual authority to bind the principal.
The duty of an agent to act always in the best interest of the principal, to avoid self-dealing.
A doctrine under which the employer is liable for torts committed by the employee in the scope of employment.
Liability incurred indirectly through the actions of another.
Treating employees or job applicants unequally on the basis of race, color, national origin, religion, sex (gender, pregnancy, or orientation), age, or disability; prohibited by federal statutes and many state statutes.


