83 Evaluating Sources
Thinking Critically About Sources

This section teaches how to identify relevant and credible sources that you have most likely turned up on the Web and on your results pages of the library catalog, Google Scholar, and specialized databases. Relevant, credible sources will meet the information needs of your of your research project.
In order to evaluate a source, you have to answer two questions about it:
- Is this source relevant to my research question?
- Is this a credible source– a source my audience and I should be able to believe?
It’s important to determine relevance before credibility because no mater how credible a source is, if it’s not relevant to your research question it’s useless to you for this project.
TIP: Other Criteria from Your Professor
Don’t forget that you also have to make sure your sources meet any other criteria that your professor may have given you for this assignment. For instance, professors often stipulate that, some of your sources have to be scholarly sources or articles from a particular database.
So make sure you have identified enough of the kind of sources your professor has requested.
You might already be worrying about how long evaluating sources is going to take. So let’s say right off that you won’t have to read all of a source to decide whether it is relevant and credible. (Later, of course, it will take a closer read to determine what direct quotes, paraphrases, and summaries you may want to use from the sources you have selected.)
Nonetheless, our advice is to not begrudge the time you spend evaluating sources. It’s one of the most important things to learn at college—the opportunity to evaluate sources is one of the big reasons your professors assign research projects. And your future employers will expect you to have learned how to do it. For the rest of your professional and personal life, you will be using the critical thinking skills that make choosing the right sources possible. So learning those skills is a good investment.
Happily, you’ll also get faster the more you do it.
ACTIVITY: Evaluation Basics
Making Inferences: Good Enough for Your Purpose?
Sources should always be evaluated relative to your purpos – why you’re looking for information. But because there often aren’t clear-cut answers when you evaluate sources, most of the time it is inferences – educated guesses from available clues – that you have to make about whether to use information from particular sources.
Your information needs will dictate:
- What kind of information will help.
- How serious you consider the consequences of making a mistake by using information that turns out to be inaccurate. When the consequences aren’t very serious, it’s easier to decide a source and its information are good enough for your purpose. Of course, there’s a lot to be said for always having accurate information, regardless.
- How hard you’re willing to work to get the credible, timely information that suits your purpose. (What you’re learning here will make it easier.)
Thus, your standards for relevance and credibility may vary, depending on whether you need, say,:
- Information about a personal health problem.
- An image you can use on a poster.
- Evidence to win a bet with a rival in the dorm.
- Dates and times a movie is showing locally.
- A game to have fun with.
- Evidence for your argument in a term paper.
For your research assignments or a health problem, the consequences may be great if you use information that is not relevant or not credible.
Activity: Quick Check
Instructions: Select one answer to each question.
Open activity in a web browser.
Evaluating for Relevancy
Relevant sources are those that pertain to your research question. You’ll be able to figure that out fairly quickly by reading or skimming particular parts of sources and maybe jotting down little tables that help you keep track. We’ll show you how below, including where to look in specific kinds of sources and what questions to ask yourself as you do.
One thing to consider early on as you make inferences about relevancy is the effect that timeliness, or a source’s currency, should have on deciding whether a source is relevant. Your research question will determine that.
For instance, if your research question is about the life sciences, you probably should consider only the most recent sources relevant because the life sciences are changing so quickly. There is a good chance that anything but the most recent sources may be out of date. So aim for sources no more than 5 years old. (An example discipline that calls for even newer sources is computer security.)
But suppose your research question is about the Edo Period in Japan (1603-1868) or about Robert Falcon Scott, who explored the Antarctic from 1901-1913. In these cases, an item from 1918 might be just as useful as an item from 2018 (although new information may have been found in the 100 year gap). But something from 1899 about Antarctica or from 1597 about Japan would NOT be current enough for these research questions.
These example research questions also give you two more clues about how to treat the timeliness or currency of sources as you consider relevance:
- Because of how long ago they lived or occurred, it would be unusual for many sources on Robert Scott or the Edo Period to have been published very recently. So, unlike sources for the life sciences, whether a source is very recent should probably not determine its relevancy to those research questions.
- Primary sources might be considered especially relevant to all three research questions. Life science journal articles that provide research findings for the first time count as primary sources. And primary sources (such as Scott’s diaries and expedition photographs, as well as paintings, literature, clothing, and household items from the Edo Period) go a long way to explain faraway people and times. (See Primary, Secondary, & Tertiary Sources.)
EXAMPLE: Currency
Check out how currency is handled on TED. This site provides videos of speakers talking about new ideas in technology, entertainment, and design. (That’s what TED stands for.) Some videos are labeled “Newest Talks,” and TED tells when every video was recorded.
For your sources for which timeliness matters, see the section Where to Look, which includes where to look in websites, articles, and books for information about a source’s currency.
Time-Saving Tips
Instead of thinking you have to read all of every source in order to figure out whether it is relevant, read or skim only parts of each source. If you’re looking at the right parts, that should give you enough information to make an educated guess about relevancy.
But what should you be looking for as you do that reading and skimming? One way to figure that out is to first parse your research question so that you can figure out its main concepts. (This is like identifying main concepts in your research question in order to search precisely.)
For instance, suppose your research question is: How does having diverse members in a group increase the critical thinking of the group?
What are this question’s main concepts? Our answer is: group diversity and critical thinking.
So when trying to judge which sources are relevant to these main concepts, you would assess whether each source you’ve found pertains to at least one of these concepts. We recommend you jot down a little table like the one in the example below to keep track of which sources address each main concept.
To be considered relevant to your research question, a source wouldn’t necessarily have to cover all of your main concepts, but finding sources that do is the ideal. Otherwise, you just have to make do with what you’ve got. Don’t forget that each source would have to pass the currency test, too, if currency is important to your research question. So it’s wise to record your decisions about the sources’ currency on your tables, too.
EXAMPLE: Sources’ Main Concepts and Currency
Research question: How does having diverse members in a group increase the critical thinking of the group?
| Currency Okay | Group Diversity | Critical Thinking | |
| Source A title | X | X | |
| Source B title | X | ||
| Source C title | X | X | X |
The table in this hypothetical example indicates that both Sources A and C are relevant because each pertains to at least one main concept from the research question. Currency doesn’t seem to matter much to our research question, so all three sources were marked current. But since currency is all that Source B has to offer, it is not relevant for this project.
If you do make little tables for relevance, it’s probably a good idea to hang on to them. You might find them helpful later in your research process.
Where to Look in Websites, Articles, and Books
The information below tells where to look and what questions to ask yourself to assess three kinds of sources’ relevancy to your research question. Whatever you do, don’t stop evaluating a source after looking only a website’s name or the title of another source.
Save time by looking in particular places in sources for information that will help you figure out whether the source is relevant to your research project. Much of our advice below comes from “Speedy Reading” in The Craft of Research, second edition, by Wayne Booth, Gregory Colomb, and Joseph Williams, 2003, pp. 108-109.
On a website, check the name of the website and its articles for clues that they contain material relevant to your research question. Consider whether time should have an impact on what information can be considered relevant. If so, skim any dates, datelines, What’s New pages, and press releases to see whether any website content works with the time considerations you need. Page creation or revision dates that you find can also help.
Skim any site map and index on the website for key words related to your research question. Try the key words of your research question in the search box. Do you see enough content about your keywords to make you think parts of the website could be helpful?
For an article, think about the title. Does it have anything to do with your research question? Consider whether time should have an impact on what sources can be considered relevant. If so, is the publication date within your parameters? Also skim the abstract to see whether the article works with the time considerations you need. For instance, if there is a time period in your research question, does the article address the same time period or was it created in that time period?
Look at the abstract and section headings in the article to locate the problem or question that the article addresses, its solution, and the outline of the article’s argument for its main claim. Can those help answer your research question? Do they make it seem the article will give you information about what others have written about your research question? Do they offer a description of the situation surrounding your research question?
Do the article’s introduction and conclusion sections help you answer your research question and/or offer a description of the situation surrounding your question so you can explain in your final product why the question is important? Check whether the bibliography contains keywords related to your research question. Do the sources cited by the bibliography pertain to your research question?
For a book, check whether the title indicates the book could be about your research question. Consider whether time should have an impact on what sources can be considered relevant. If so, is the publication date or copyright date (usually listed in the library catalog or on the back of the book’s title page) too early or late for any time constraints in your research question? Maybe it is just right. Also skim some of the preface and introduction to see whether the book works with the time considerations you need.
For help answering your research question, skim the book’s table of contents and any summary chapters to locate the problem or question that the book addresses, its solution, and the broad outline of the book’s argument for its main claim. Do they also give you information about what others have written about your research question? Do they offer a description of the situation surrounding your research question? Look for your key words in the bibliography. Do the sources cited pertain to your research question? Skim the index for topics with the most page references. Do the topics with the most page references pertain to your research question?
ACTIVITY: Follow a Title’s Clues for Relevance
ACTIVITY: Connecting the Dots beyond the Title
Open activity in a Web browser.
Connecting the Dots beyond the Title
Instructions: Now you can practice evaluating for relevance beyond the title. In the previous activity, you evaluated for currency and relevance the tittles of three sources for the research question: How does “prospect theory” in behavioral economics help explain medical doctors’ decisinos to favor surgery or radiation to cure cancer in patients?
Judging by the title, the most relevant source for that research question seemed to be a journal article called “Cancer Treatment Prescription–Advancing Prospect Theory beyond Economics,” in Journal of The American Medical Association Oncology, June, 2016.
Read the abstract of the article below. Then decide whether this source is relevant to your research questions above. That is, might the article help you meet any of your project’s information needs about the research questions? If there is at least one need it can help meet, then you should judge the article relevant.
Answer the question below the abstract to indicate the source is relevant. Then compare your answer with our feedback.
As usual, your information needs are:
- To learn more background information.
- To answer your research question.
- To convince your audience that your answer is correct or, at least, the most reasonable answer.
- To describe the situation surrounding your research question for your audience and explain why it’s important.
- To report what others have said about question, including any different answers to your research question.
Abstract
“Cancer Treatment Prescription–Advancing Prospect Theory beyond Economics,” in Journal of The American Medical Association Oncology, June, 2016 (Note to students: This article and abstract are fictitious.)
Importance Cancer Treatment is complex. We expect oncologists to make treatment decisions according to definitive standards of care. Finding out that prospect theory demonstrates that they react very much like most other people when deciding to recommend surgery or chemotherapy for their patients indicates that more self-reflection on oncologists’ part could help patients make better decisions. (Prospect theory describes how people choose between alternatives that have risk when the probability of different outcomes is unknown.)
Objective To show whether prospect theory applies to how oncologists framed their recommendations for surgery or chemotherapy for patients in good condition and bad condition.
Design, Settings, and Participants Records of 100 U.S. oncologists were examined for the years 2014 and 2015, which documented patient conditions and the way oncologists framed their recommendations regarding surgery or chemotherapy. Thus, a quasi-experimental ex post facto design was used for the study.
Main Outcomes and Measures This study explored the relationship between the way in which the oncologists “framed” the choice of surgery or chemotherapy as they made recommendations to patients, to patients’ conditions, and the choice actually made. Those results were compared to what prospect theory would predict for this situation.
Results Physicians seemed to present their recommendation of surgery or chemotherapy in a loss frame (e.g., “This is likely to happen to you if you don’t have this procedure”) when patients’ conditions were poor and in a gain frame (e.g., “By having this procedure, you can probably dramatically cut your chances of reoccurrence”) when their conditions were less poor. These results are what prospect theory would have predicted.
Conclusions and Relevance This study opens up the possibility that, as described by prospect theory, a person’s choice of framing behavior is not limited to how we naturally act for ourselves but includes how we act for other people, as the oncologists were acting on behalf of their patients. More research is necessary to confirm this line of evidence and determine whether oncologists’ decision making and framing is the most effective and entirely according to the best standards of care.
Evaluating for Credibility
Next, you’ll be evaluating each of the sources that you deemed relevant.
What are the clues for inferring a source’s credibility? Let’s start with evaluating websites, since we all do so much of our research online. But we’ll also include where to find clues relevant to sources in other formats when they differ from what’s good to use with websites. Looking at specific places in the sources will mean you don’t have to read all of every resource to determine its worth to you.
And remember, the more you take these steps, the faster it goes because always examining your sources becomes second nature.
What Used to Help
It used to be easier to draw conclusions about an information source’s credibility, depending on whether it was a print source or a web source. We knew we had to be more careful about information on the web–simply because all the filters that promoted accuracy involved in the print publishing process were absent from most web publishing. After all, it takes very little money, skill, and responsible intent to put content on the web, compared with what has to be done to convince print publishers that your content is accurate and that they will make money by printing it.
However, many publishers who once provided only print materials have now turned to the web and have brought along their rigorous standards for accuracy. Among them are the publishers of government, university, and scholarly (peer-reviewed) journal websites. Sites for U.S. mainline news organizations also strive for accuracy rather than persuasion–because they know their readers have traditionally expected it. All in all, more websites now take appropriate care for accuracy than what used to be true on the web.
Nonetheless, it still remains very easy and inexpensive to publish on the web without any of the filters associated with print. So we all still need the critical thinking skills you’ll learn here to determine whether websites’ information is credible enough to suit your purpose.
5 Factors to Consider
Evaluating a website for credibility means considering the five factors below in relation to your purpose for the information. These factors are what you should gather clues about and use to decide whether a site is right for your purpose.
- The source’s neighborhood on the web.
- Author and/or publisher’s background.
- The degree of bias.
- Recognition from others.
- Thoroughness of the content.
How many factors you consider at any one time depends on your purpose when seeking information. In other words, you’ll consider all five factors when you’re looking for information for a research project or other high-stakes situation where making mistakes have serious consequences. But you might consider only the first three factors at other times.
A Source’s Neighborhood
To understand this concept and begin to use it, imagine that all the sites on the web constitute a community. Just like in a geographical community, there are neighborhoods in which individual sites hang out.
Thinking about what neighborhood a source is in on the web can help you decide whether the site is credible and suits your purpose.
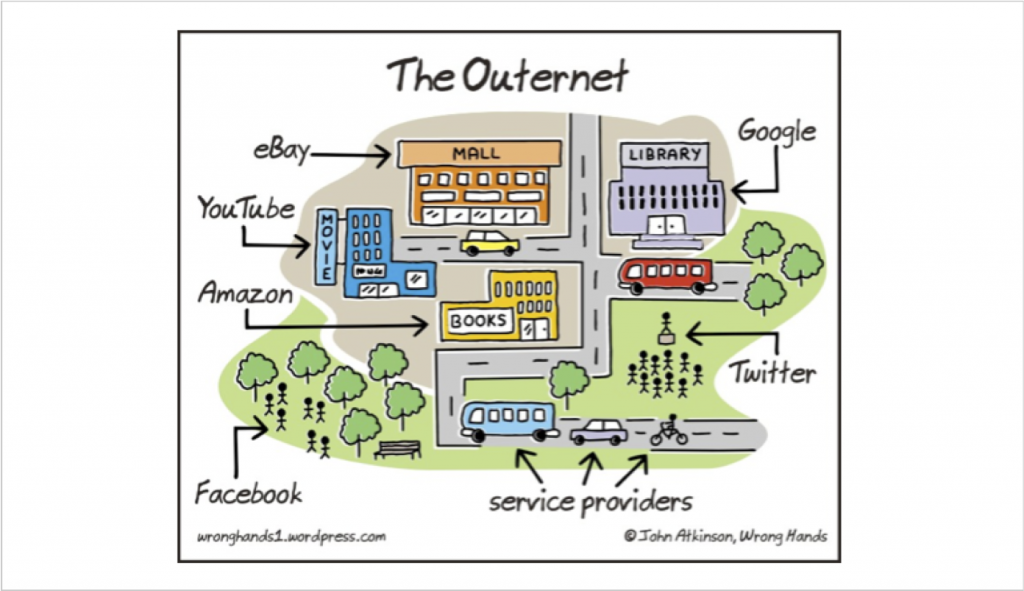
Wrong Hands)
Audio: Neighborhoods on the Web
Listen to the audio clip (or read the text version) to hear how intuitive this concept is. After you listen, the next activity will show you how to apply the concept.
Tip: Author’s Purpose for Print
Rather than examine print sources for their web neighborhood, examine them for their author’s purpose. Read the introduction and conclusion and look at the table of contents to discern the author’s purpose.
For instance, did the author intend to use the book or magazine article to inform/educate, persuade, sell, or entertain?
And is the author’s purpose suitable for your purpose? For instance, does the fact that a resource was intended to persuade mean it can’t help you answer your research question? (As you know from Sources and Information Needs, yes.)
Activity: Self-Check
Why might you want to read information on an advocacy site (from the neighborhood of sites that promote particular ideas and behavior)—even when you’re writing a term paper and it’s not acceptable to cite that source because it persuades instead of educates and is not objective? See the bottom of the page for the answer.
Clues About a Website’s Neighborhood
Watch the Understanding Google Search Results movie to better understand how you can quickly determine what kind of information you’ve turned up in a Google search.
Movie: Understanding Google Search Results (no audio)
[iframe src=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/mw1sYYGS_PU?rel=0″ width=”560″ height=”315″ allowfullscreen=”allowfullscreen”]
On a website, check pages labeled About Us, About This Site, Mission, Site Index, and Site Map, if available. (If such pages or similarly labeled ones don’t exist, it may be a sign that the site may be less trustworthy.)
Ask yourself these questions to gather clues that will help you decide what neighborhood you’re in:
- Is the site selling products and/or services (even if there are articles and other useful information, too)? Perhaps it’s a retail, service center, or corporate site.
- Are there membership applications and requests for contributions of money or time anywhere on the site? They’re usually a sign that you’re on a site that promotes particular ideas or behavior – in other words, they’re in the advocacy neighborhood.
- Do postings, articles, reports, and/or policy papers give a one-sided view or multiple views on issues, people, and events? If they’re one-sided, the site is probably a commercial site or in the advocacy group neighborhood. If the information is even-handed and includes different sides of an issue, the site is more likely to be on the library/museum, school, or mainline U.S. news side of town. Sites there usually provide information designed to educate rather than persuade. Newspapers online or in print usually do have editorial pages, however. But labeling opinions as such helps keep mainline U.S. news sources in the newsstand neighborhood and out of the advocacy neighborhood.
Activity: Neighborhoods on the Web
Work through the three activities below to practice the concept of neighborhoods on the web.
Matching Site to Neighborhood – Open activity in a web browser.
Matching Neighborhood to Purpose – Open activity in a web browser.
Which Neighborhood? – Open activity in a web browser.
Example: Check Them Out
Think we’re making a mountain out of a molehill about being careful about web sources? Please click the links below to look at three websites. Is there an inference(s) you can make that applies to all three? Perhaps that whether a website looks professionally done is not enough to insure that it is credible.
- RYT Hospital: Dwayne Medical Center – http://rythospital.com
- Dog Island – http://www.thedogisland.com
- The Manhattan Airport Foundation – http://manhattanairport.org
Making the Inference
Consider the clues. Then decide the extent that the site’s neighborhood is acceptable for your purpose. It might help to grade the extent that this factor contributes to the site being suitable on a scale like this one:
- A – Very Acceptable
- B – Good, but could be better
- C – OK in a pinch
- D – Marginal
- F – Unacceptable
You’ll want to make a note of the resource’s grade for neighborhood so you can combine it later with the grades you give the other factors.
Answer to Activity: Self-Check
The answer to the “Self-Check” Activity above is:
Advocacy sites are useful to learn about a particular viewpoint. They may provide a wealth of information—you just have to keep in mind that it’s just one side’s view and then also seek out the other side’s view.

